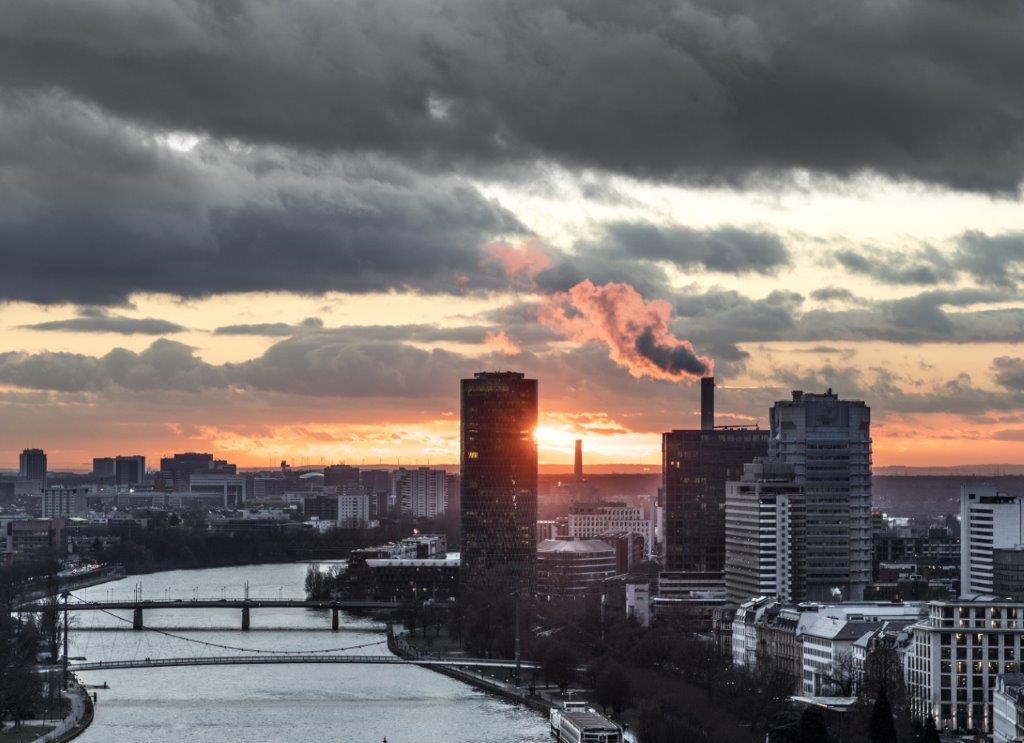
Air pollution from smog and fine dust
Regular uptake of smog and fine dust can pose health risks for humans. It is well known that these pollutants are more common in metropolises such as Beijing and Los Angeles.
But in Germany, too, it is not uncommon for the limits with regard to pollutant values to be exceeded, which is why the issue of air pollution in large cities is becoming more and more of a problem. Fine dust pollution is also increasing indoors. The questions are what smog and particulate matter are, how they arise and, above all, what consequences they have and how you can protect yourself against them.
What is smog
Smog was originally a mixture of smoke and fog, which is why the name is made up of the two English words “smoke” and “fog”. Today the term smog is used much more generally and stands for several types of air pollution that are caused by emissions. Smog can be divided into three types: “classic” smog, summer smog and electrosmog.
The "classic" smog
Der „klassische Smog“, auch London-Smog oder Wintersmog genannt, wird durch die Luftschadstoffe Ruß und Schwefeldioxid verursacht. Diese entstehen bei der Verbrennung schwefelhaltiger Kohle. Diese Verschmutzung der Luft ist schon recht lange bekannt. Bereits im Jahre 1952 sind ihm 12.000 Menschen in der Stadt London zum Opfer gefallen. Nur 10 Jahre später starben auch im Ruhrgebiert 150 Menschen an den Folgen von Smog.
Dank der verbesserten Rauchgasreinigung hat sich das Aufkommen von Smog in dieser reinen Konzentration aus Ruß und Schwefeldioxid deutlich vermindert. Aber selbst heute lassen sich noch Dunstwolken über großen Städten und Industriegeländen beobachten, welche neben Ruß und Schwefeldioxid mit weiteren schädlichen Gasen wie Kohlenstoffmonoxid und Stickstoffoxid gefüllt sind.

These pollutants are mostly caused by unfiltered and uncleaned exhaust gases from industrial plants, thermal power plants, wood-burning systems and vehicles with internal combustion engines. Such an existing cloud of vapor is a clear sign of environmental pollution, but not yet smog. The formation of smog must be favored by a weather situation with little exchange. Usually the lowest layer of air on the ground is the warmest, as the earth absorbs and stores the heat of the sun. This warm air rises and cools down as the altitude increases. At the same time, the pollutants are transported upwards with the warm, rising air. In the so-called inversion weather situation, which occurs more frequently in the winter months, the air layers behave in reverse. This means that the upper layers of air are warmer than the lower layers of air. In addition, the occurrence of wind in this weather situation is very low. As a result, the lowest layer of air cannot rise, there is no exchange of air and the pollutants cannot be transported upwards. As a result, the cold air enriched with pollutants remains stuck near the ground.
The summer smog

If there is an increased formation of ozone near the ground, one speaks of summer smog. This is also known as photochemical smog or Los Angeles smog. This type of smog is also favored by certain weather conditions. In this case it is a period of fine weather lasting several days. The intense UV radiation combines with pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, hydrogen peroxides and carbon monoxide. This creates an increased concentration of photo-oxidants such as ozone. Above all, nitrogen oxides are mainly given off by motor vehicles and power plants.
The electrosmog

Electric and magnetic fields are generated in the vicinity of electrical lines and devices such as televisions, smartphones, microwave ovens and electric stoves.
An increased occurrence of electric and magnetic fields is also considered to be air pollution and is referred to as electrosmog. Although the health impairments caused by electrosmog are still controversial, there are limit values that have been set by the committee of the German Electrotechnical Commission.
What is particulate matter?
In both winter and summer smog, toxic gases are produced by the combustion processes of motor vehicles and industrial plants. These combustion processes not only create toxic gases, but also fine dust. Fine dust refers to solid particles that can float in the air for a long time and are smaller than 10 micrometers. In addition to the man-made sources, there is also a natural occurrence of fine dust, such as fungal spores, pollen, volcanic ash and much more.
Fine dust is categorized into three different sizes: PM10 (PM = particulate matter), PM2.5 and PM0.1. Particles with a size of PM10 have a maximum diameter of 10 micrometers and are inhalable for humans. Fine dust of the categories PM2.5 and PM0.1 can penetrate even deeper into the human organism and are referred to as respirable dust or also as ultra-fine dust.
Health risksthrough smog and fine dust pollution
The effects of air pollution can be very different. A high incidence of smog also means an increased risk of absorbing fine dust, since smog and fine dust are related. Particles with a size of 5-10 micrometers can enter the bronchi through the nasopharynx. Smaller particles with a diameter of 3 micrometers get into the bronchioles and alveoli. Ultra-fine dust particles even penetrate into the lung tissue. There they can only be removed with great difficulty or not at all.
Inhaling the harmful gases in conjunction with fine dust can cause health consequences such as cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. There is also evidence that ultrafine dust can reach the brain via the olfactory nerve. Especially in children and the elderly who are exposed to high levels of polluted air, both intelligence and memory can be impaired.

A particularly endangered risk group are people regardless of age who already suffer from a respiratory disease. These include bronchitis and asthma or allergies such as hay fever. Under the influence of air pollutants, it is possible for these symptoms and diseases to worsen. The risk group also includes people with cardiovascular problems.
Furthermore, the uptake of nitrogen dioxide, which is mainly emitted by diesel vehicles, can express symptoms such as headaches, dizziness and shortness of breath.
Smog and fine dust pollution in Germany
In January 1979, a smog alarm of level one was issued for the first time in Germany in the Ruhr area, the lowest level of three alarm levels. As a result, all citizens have been asked to refrain from activities that pollute the air even more. Only six years later, another smog alarm was triggered for the Ruhr area, but this time with level three. This was followed by a driving ban for several hours and various restrictions for industrial companies.
These harmful emissions have been significantly reduced in the last few decades. Both the concentration of ozone in summer and the values for sulfur dioxide in winter have decreased. Among other things, measures such as environmental zones in cities and the labeling of vehicles with environmental badges have contributed to this. However, the health effects of air pollution should not be neglected.
In parallel to the improvement in air quality in Germany, however, the background concentration continues to increase. The background concentration is understood to mean air pollution that is “imported” to Germany by air masses from Asia and Africa. This is especially true for ozone, which can remain in the atmosphere for around three weeks.

But what is it that pollutes the air the most?
Despite all the improvements, nitrogen oxides and particulate matter remain a threat to the environment and human health. These air pollution are already clearly noticeable in some cities in Germany.
The occurrence of nitrogen oxides and fine dust is greatest at the Neckartor in Stuttgart and in 2016 had an average nitrogen oxide content of 82 micrograms per cubic meter of air. This means that this value is twice as high as the established limit of 40 micrograms per cubic meter. These exceedances result in occasional driving bans in certain areas of the city of Stuttgart. But other cities such as Munich, Kiel, Cologne, Hamburg and Reutlingen have regularly exceeded the reference value so far.
Particulate matter in interiors
The occurrence of fine dust is also an important issue in living rooms and offices, after all, most people spend a lot of time in closed rooms. Particulate matter not only penetrates inside from the street, but can also arise directly in the room through certain sources. These sources include tobacco smoke and candle soot, among others. But activities such as cooking, roasting or people staying in rooms can also generate or stir up fine dust. Computers, copiers and printers are additional modern sources of fine dust. Especially in winter, increased heating can lead to a particularly high concentration of fine dust in the interior.
Measures to protect against fine dust indoors
The first measure to counteract the formation and spread of fine dust is to wipe and vacuum the floors regularly. Especially when wiping or dusting, it is important to ensure that this is done with a damp cloth. A dry duster would only stir up the fine dust and not remove it.
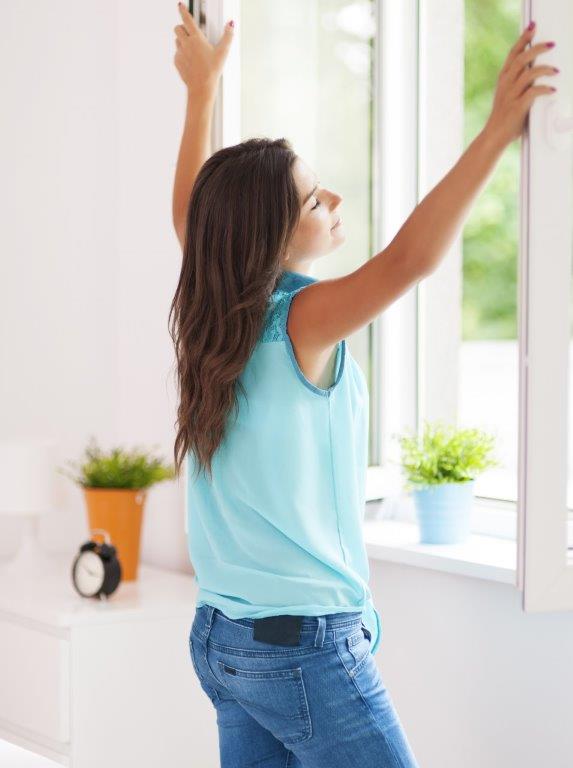

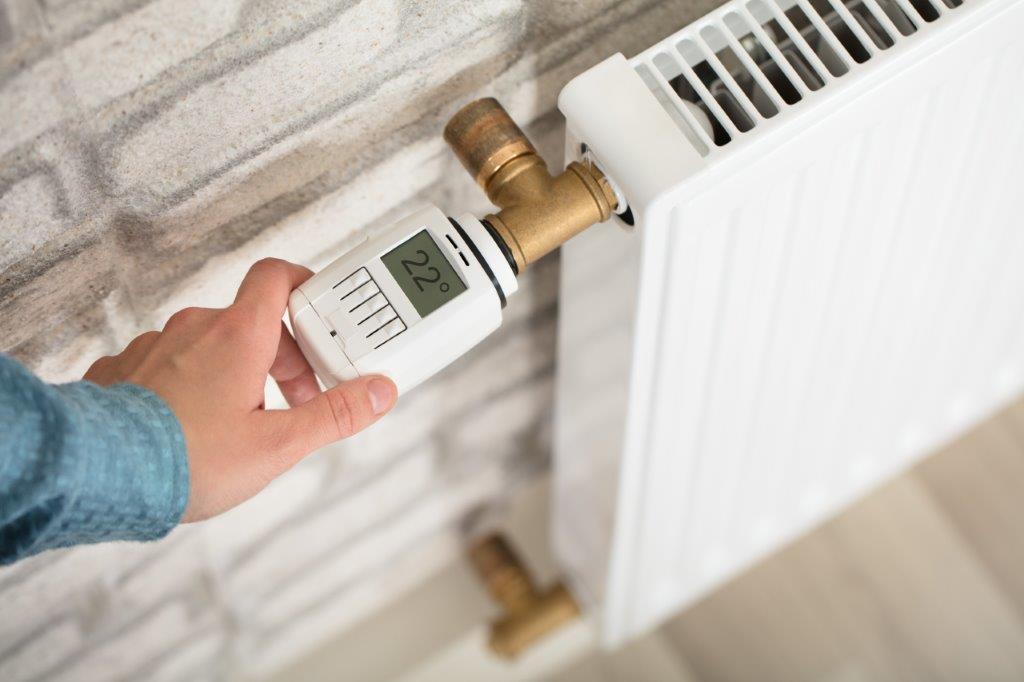
In order to create an exchange of air indoors, it is important to ventilate properly. In winter it should be ventilated briefly but intensively several times. Correct heating also plays a role here. The room temperature should not be more than 22 degrees and the room air should not be too dry, as the dust can be whirled up more quickly in dry rooms. When using wood heating, it is advisable to pay attention to symbols such as the Blue Angel, as these are particularly low in pollutants. If there is an extractor hood in the kitchen, it should be used until shortly after cooking.

Burning candles and tobacco also creates fine dust. Consequently, smoking and burning candles or incense sticks should be avoided in enclosed spaces.
Air purifiers are an already established tool in other countries such as China, the U.S.A., Canada and England to combat fine dust. These partially filter up to 95 percent of the dust particles from the air in the room.
However, this does not mean that the air is only 5 percent polluted with fine dust, as new ones are constantly being created. However, halving the particulate matter concentration is quite conceivable. Decentralized ventilation systems can also help to remove air that is enriched with pollutants and fine dust and to permanently supply the living space with healthy, clean air. In addition to cleaning the air, such a ventilation system also ensures the correct moisture content (link article humidity?) Of the air.
ConclusionAir pollution from smog and fine dust
The smog and fine dust pollution in Germany (pollution of the air) has already been improved by means of environmental zones and green stickers. Nevertheless, it is important to be careful not to expose yourself to high levels of air pollution on a regular basis in order to avoid health consequences. This is easy to do by integrating proper ventilation, heating and regular dusting as a ritual in everyday life. In heavily polluted urban districts, helpers such as air purifiers and decentralized ventilation systems in the house can provide great help in avoiding fine dust. Other effects of air pollution were discussed in detail in the guide.
But you should not only think about avoiding or removing fine dust in your own living space. One way or the other by bike instead of by car contributes to the fact that the air that enters the living space from outside is cleaner and therefore also healthier.