Humidity in living spaces
The correct humidity of the air is an important comfort factor in living space – both too high and too low humidity can have a negative impact. Each room has its own optimum humidity, depending on its use and condition.
This article provides basic information on this topic and highlights the optimal humidity for different living spaces. In addition, the consequences of too high and too low values on people and the building fabric are shown. Furthermore, tips are given on how this optimal value can be achieved with different means and how you can measure the humidity.

Absolute, relative and optimal humidity
Simply put, the term humidity, or humidity for short, means the proportion of water vapor in the ambient air. For a more precise definition, this term is divided into absolute and relative humidity.
The absolute humidity is the simple indication of how many grams of water are in one cubic meter of air. The determination of the relative humidity is more complicated because it indicates what percentage of the maximum water vapor content is currently in the air.
It is important to know that the air can only hold a certain amount of water. How large this amount is depends very much on the temperature. Cold air absorbs less water vapor than warm air. The rule here is: the higher the temperature, the more water vapor the air can absorb.

At a temperature of zero degrees Celsius, the air can absorb five grams of water vapor per cubic meter. At a much warmer temperature, such as 30 degrees, this is already 30 grams.These gram numbers represent the maximum content of water vapor that the air can absorb at the corresponding temperature. However, in order to determine the value of the relative humidity, both the absolute and the maximum humidity are required.
The optimal air humidity is in turn not a fixed value, but a percentage range of the amount of air humidity that is harmless to both the health and the structure of the living space. In combination with the right temperature, these two factors create the ideal indoor climate.
The optimal humidity in different living spaces
In general, a relative humidity of 50% and a room temperature of 20 degrees Celsius are considered to be the optimal indoor climate. However, this differs from room to room, as the room climate is influenced by various factors. On the one hand, it is crucial how many people are in the room, how long and how often. On the other hand, the activities that are carried out in the rooms play a major role. In rooms such as the bathroom and kitchen, a higher level of humidity is common due to the activities carried out in them. In comparison, the correct temperature in the basement is only 10-15 ° C, which is also reflected in the low humidity. However, too high humidity is not advisable here either.
The following information is considered to be ideal room conditions for the individual living spaces:
| Room | Optimal humidity |
Optimal temperature |
| living room and study (office) | 40-60% | 20 ° C |
| bedroom | 40-60% | 16-18 ° C |
| Children’s room | 40-60% | 20-22 ° C |
| kitchen | 50-60% | 18 ° C |
| bathroom | 50-70% | 23 ° C |
| basement | 50-65% | 10-15 ° C |
Consequences of too high or too low humidity
The temperature and humidity of the room not only contribute to well-being, but can also cause discomfort and other health consequences. In addition, the effects on the building fabric of the house should not be forgotten.
Falling below the optimal humidity

Eye, skin and mucous membrane irritations can already occur at a humidity level of less than 40 percent. This is clearly too little humidity, which manifests itself in the drying out of the skin with redness and itching. Furthermore, the immune defense is weakened, which can lead to more common colds. At a value below 23 percent, the loss of moisture can only be partially compensated for by breathing, which leads to a feeling of discomfort. Another consequence of too low a humidity level is increased light electric shocks when touching metallic objects, since dry air is electronically charged more quickly.
In addition to the health consequences, overdrying can lead to structural damage (too little humidity). Wood in particular suffers when it falls below the minimum value because it warps.
Exceeding the optimal humidity

At what level of moisture does mold start to form?
As already mentioned, a permanently too high humidity of over 60 percent can lead to the formation of mold. This is also known as what is known as a damp apartment. An infestation is almost inevitable from a humidity of 70 percent or more. The formation of mold due to high humidity not only endangers the building structure of the house, it is also dangerous for human health. Increased inhalation of mold spores can cause diseases such as asthma or allergies.
A humidity of over 80 percent also creates a perfect environment for fungi, mites and other parasites to multiply.
Improvement of the humidity in the interiorMeasure the humidity
The basis of room climate regulation is first of all to measure the correct and current humidity in the living space.
A very complex way would be to measure the absolute and maximum humidity yourself and thus calculate the value of the relative humidity. Thanks to a hygrometer, however, this method is not necessary (hygrometer humidity).
Depending on the model, hygrometers can be set up or hung up. The ideal location is neither too close to an outside wall nor to a door, window or heater. Regular measurements of the air humidity are important when determining the room climate, as various influences mean that the room humidity is occasionally too high or too low. It is only necessary to act when the room climate permanently exceeds the upper or lower limit of the respective room.

Lower the humidity in rooms
Improvement measures if the humidity is too high


Another possibility is to remove moisture from the air with the help of salt. For this purpose, several bowls filled with salt are set up in the room. The bowl should be filled to a maximum of four centimeters. For this method, simple table salt is sufficient, which must be replaced as soon as there is more water than salt in the bowl.
In addition, in the case of increased humidity in a damp apartment, the use of indoor fountains should be avoided. Aquariums or terrariums, which give off water vapor into the room air, should also be covered in summer. It is also helpful to dry the laundry outdoors. Even moving some indoor plants to the balcony or terrace during the summer can help. The extractor hood should always be used during cooking and for a while afterwards.
Excessive humidity can have a negative effect on both a person’s health and the fabric of a building. A lot of moisture in the air promotes mold growth in living spaces immensely. It is therefore essential to measure and control the air humidity regularly in order to ensure an appropriate level in the air and, if necessary, to reduce it. Bathrooms are particularly prone to mold growth, as they are usually exposed to high temperatures and a large amount of moisture in the air.


The warm air in the bathroom in particular can absorb a lot of water vapor. But the air you breathe and sweat that escapes also causes the humidity to rise in any room. It is necessary to keep the humidity in living rooms in the appropriate range, because there is a risk of mold from 60% humidity. In the following we have briefly summarized how you can reduce the humidity in rooms with simple measures.
Checklist with the best 10 tips on how to reduce the humidity in rooms
- Ventilate extensively and regularly
- Maintain optimal room temperature and do not let rooms cool down
- Keep doors closed
- Set up a bowl filled with salt, cat litter or silica sand
- Remove indoor fountains, aquariums, terrariums and indoor plants
- Use the extractor hood
- Let laundry dry outdoors
- Take a short and cold shower
- Use a dehumidifier
- Install extract air devices / ventilation systems
Improvement measures if the humidity is too low
In a dry environment, ventilation at the right moment can not only remove the air that is too dry, but also increase the humidity. Even if the humidity is too low, it should also be determined in advance on the external hygrometer whether the outside air humidity is higher than that in the interior. The process of ventilation is analogous to ventilation when the humidity is too high.
In addition, all aids can be accessed that should be avoided when the air humidity is too high. Indoor fountains, aquariums and plants give off moisture to the room air and thus improve the room climate.
Ventilation systems for the optimal indoor climate
Completely regardless of the season, decentralized ventilation systems always ensure the right room climate without any effort. Here, a hygrostat for air humidity is usually already integrated in the associated control technology.
Decentralized ventilation systems are installed in the outer walls and take over the air exchange without their own ventilation. At least two devices are required for an optimal result. One system transports the used air to the outside. The device uses a heat exchanger – a ceramic core – to prevent moisture and heat loss. While the old air is being extracted, the ceramic core maintains a healthy basic level of moisture that is created by the formation of condensation and releases it into the fresh air. In addition to the aforementioned basic moisture, the ceramic core also stores the heat contained in the air and transports this up to 93 percent back into the living space.
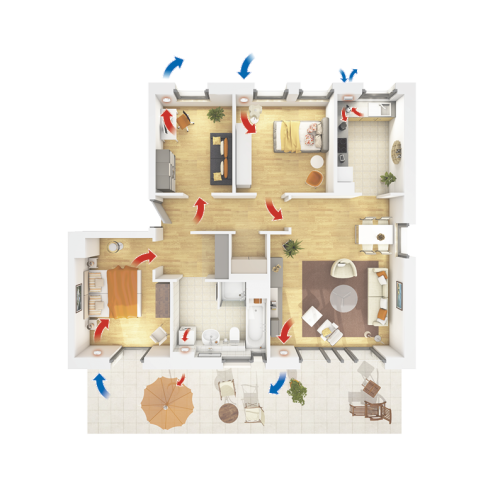
After the stale air has been removed, it takes about 70 seconds for the reversible fan to change direction and bring the fresh air into the living room. The second system works in push-pull mode, i.e. when one fan feeds fresh air into the room, the other draws the stale room air in the meantime. This opposing cooperation ensures that the room is permanently supplied with fresh air.
Conclusion - humidity
The indoor climate is a factor that not only affects the fabric of the apartment or house, but also the well-being and health of people. When regulating the climate, the relative humidity and the temperature of the rooms should be kept in mind. Occasionally exceeding or falling below the relative humidity is initially a risk factor neither for human health nor for the building fabric. However, if this condition persists, urgent measures must be taken to reduce or increase the humidity in rooms