Energetic renovation - measures and funding opportunities
Energy consumption has increased dramatically in the last few decades, not only in Germany and other industrialized countries, but all over the world. Fossil fuels such as coal, crude oil and natural gas are still the main sources of energy production. But their occurrence is gradually decreasing.
In addition, the burning of fossil fuels has an enormous impact on climate development. To counteract this, the subject of energy-efficient renovation is inevitable for all property owners. An energetic renovation not only reduces the consumption of fossil fuels, but also curbs the need for energy and thus saves money.

Necessity of an energetic renovation
With the advancement of technology and the emergence of more and more useful electronic helpers, the demand for energy is steadily increasing. In addition to the many technical innovations, outdated devices and systems also consume a lot of energy. With the increasing demand for energy, so does the CO2 concentration, which has a major impact on the environment and above all on global warming.
As a result, the energetic renovation is not only a measure to save energy and thus energy costs, but also makes an important contribution to climate protection.
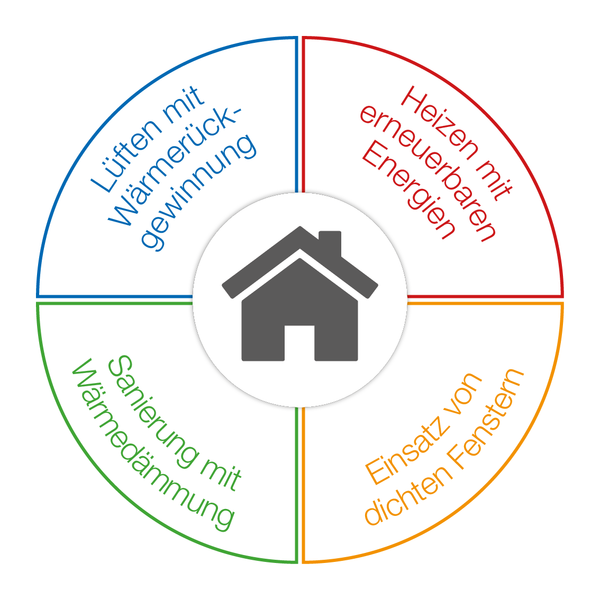
Measures for energetic renovationRefurbish energetically with thermal insulation
There are three main areas of thermal insulation:



The most important thing when it comes to thermal insulation is professional execution, which takes the physical characteristics of the facade into account. For example, when insulating the outer walls and replacing the windows, care should be taken that the windows still represent the coldest part of the facade. If this is not the case and the wall itself is the coldest point, this can lead to moisture depositing on the wall, which can lead to mold. Similar problems can also arise with interior insulation when using mineral wool without a vapor barrier. However, such difficulties can be ruled out with a prior assessment by an energy advisor.

Replacement of windows to minimize heat loss
Old windows in particular, as thermal bridges, often lead to considerable heat losses, which results in increased heating costs. These heat losses can be reduced by installing multilayer insulating glass windows. The high level of thermal protection of insulating glass is mainly due to the noble gas that is located in the space between the insulating glass panes. In addition, the window panes reflect the heat radiation, which prevents further heat loss. In addition to the pane, the frame also plays an important role.

This should have the same thermal resistance as the window sash itself. For ecological reasons, the use of tropical wood should be avoided. Modern windows not only help to reduce heat loss, but can also help to generate heat.
In winter, large south-facing windows can be used to generate heat when the sunlight is favorable. In summer, on the other hand, these large window areas can possibly overheat the rooms, which means that sun protection, ventilation or air conditioning is necessary. Such interactions must be taken into account both when planning a new building and when renovating an old building.
Heating with renewable energies
The burning of fossil fuels can be reduced or avoided entirely through the use of renewable energies. In addition, the emission of carbon dioxide, which is produced by burning fossil fuels, is reduced. Renewable energy can be generated using solar heat, biomass or a heat pump.
For the use of solar heat, a solar thermal system is required, whose roof-mounted collectors convert the solar radiation into usable heat. This is absorbed by a water-antifreeze mixture and diverted by the circulation pump into a water storage tank. The heat in the storage tank is then transferred to the drinking water via a heat exchanger. As a rule, the solar heating system is completely sufficient for heating drinking water in summer. In winter, however, the heating still has to be used. As a result, a solar system is able to heat the drinking water up to 70 percent. However, the heating demand is only covered by larger systems, and then not completely. The collectors required to generate solar heat should ideally be installed at a 45-degree angle to the south side.
Biomass can be obtained from specially cultivated energy crops, wood or from residual materials such as straw, harvest waste, organic waste and liquid manure. To generate heat in private households, however, only the use of a pellet heating system is suitable, in which pellets from natural waste wood are burned. These pellet central heating systems can replace the conventional oil and natural gas heating systems. In addition, the environmentally friendly pellet heating systems are equally user-friendly.
Heating systems with heat pumps, which have been in use for around 30 years, are technically mature and also reliable. These heating systems absorb the heat either from the groundwater in the ground or from the ambient air and transfer it to the heating system or the water to be heated. Since the temperatures in the groundwater are more constant, geothermal heat pumps are more efficient than pumps that draw their heat from the ambient air.
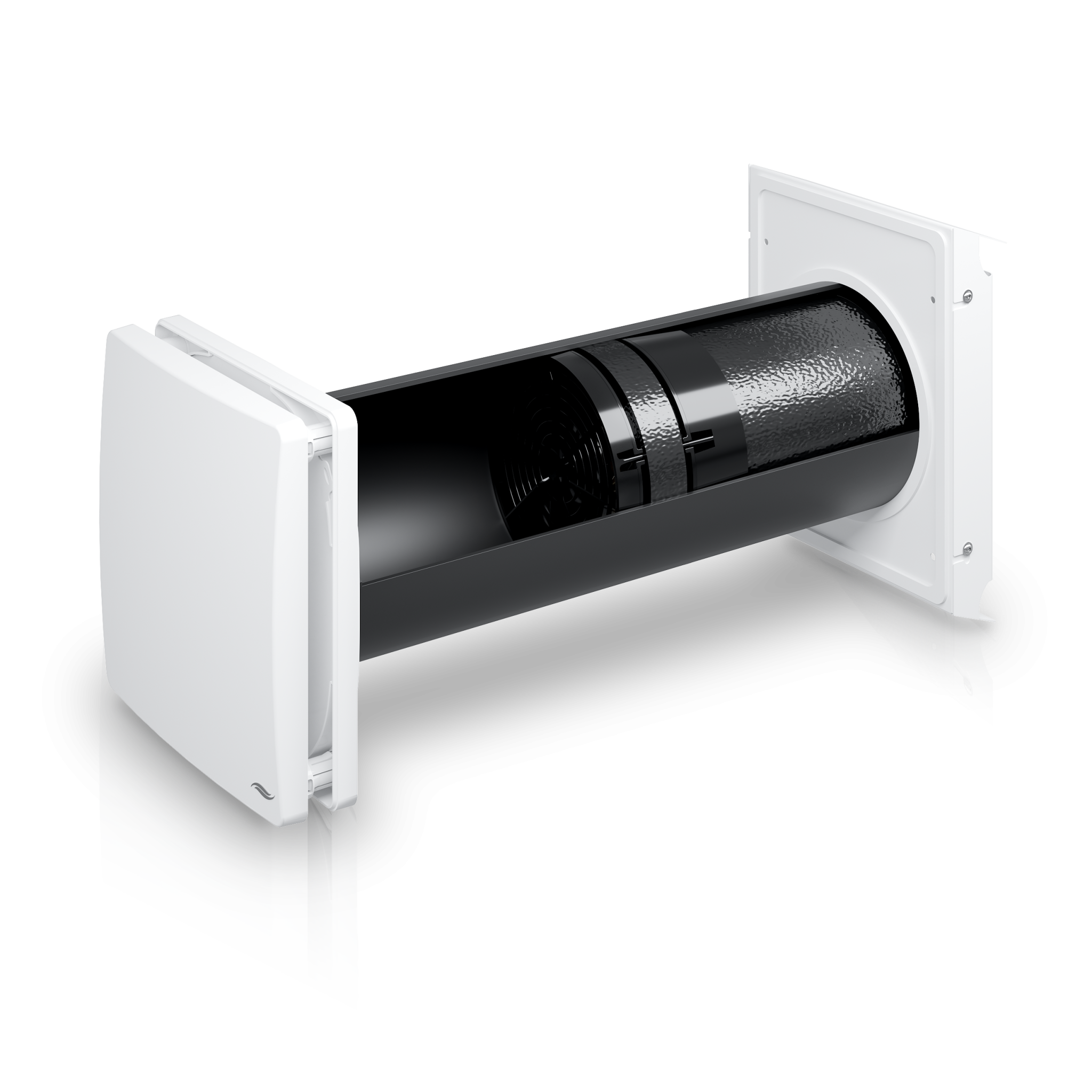
Decentralized ventilation systems for heat retention
Decentralized ventilation systems do not produce any energy or heat, but they are very helpful in keeping the warmth and fresh air in the house. By installing decentralized ventilation systems, the interior spaces are always supplied with fresh air without having to open a window for ventilation. This prevents the warm room air from escaping to the outside by opening the windows, especially in winter. The decentralized ventilation system transports the stale air and the excess moisture it contains to the outside and in return supplies fresh new air. Thanks to the ceramic heat accumulator built into the system, a large part of the heat present in the exhaust air is also given back to the room, which largely prevents heat loss. You can find out more about the principle of heat recovery here.

Energy advice in the course of an energetic renovation

Before starting an energetic renovation of your own four walls, an energy advisor should be consulted. This helps to determine the actual condition of the property and to derive the appropriate measures from it.
Energy advice offers from the consumer center are a cost-effective option.
These are represented on the Internet with a respective website or with several advice centers per federal state. The consumer protection centers deal with all topics to optimize private energy consumption such as thermal protection, power saving or heating technology. Advice is possible both in the advice center and in-house on site. These offer a basic, building, heating, solar heating or detailed check of your own house. The services cost between 10 and 40 euros.
If you need more detailed advice, you have to spend a little more money on it. An energy expert approved by BAFA should be commissioned, as this advice is eligible and can therefore be subsidized with up to 60 percent. The advisor must apply for funding himself.
Funding programs for energetic renovation
The energetic renovation does not necessarily represent an option for homeowners. The EnEV (Energy Saving Ordinance) also imposes certain obligations on homeowners on energy renovation. Accordingly, there are various subsidies for energy-efficient renovation measures. House owners who exceed the minimum requirements of the EnEV are particularly encouraged. In conjunction with the KfW development bank, low-interest loans can be taken out for energy-efficient renovation projects. These support both individual renovation measures and complete renovations. In addition, a higher loan amount can be taken out if the project meets the requirements of the “KfW Efficiency House”. In addition to loans, KfW offers a subsidy funded by the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy for anyone who undertakes energy renovation without a loan.

Conclusion - energetic renovation
Bringing your home energetically up to date initially causes relatively high costs, but one can definitely speak of a real investment. But owning outdated systems is also becoming more and more expensive, as fossil fuels are becoming more and more expensive due to the increasing scarcity. In the medium to long term, the energetic renovation is therefore also financially worthwhile. In addition, the increase in the value of your own property, which was created through the energetic renovation, can be seen as an advantage. In addition, the comfort of living in your own home increases, as professionally executed thermal insulation has positive side effects, such as soundproofing and moisture protection. In addition, an energetic renovation improves both fire protection and the life of the building structure in many cases.