Prevention and avoidance of mold
If mold has appeared in living spaces, this means not only annoying and sometimes expensive measures to remove it, but also a health hazard. In addition to structural defects or third-party negligence, mold can in many cases be attributed to incorrect heating and ventilation in the apartment.
If the mold is discovered, it is usually too late, because the visible brown or black spots on the walls or the furniture can be the offshoot of deep-seated mold that is in the interior of walls, upholstery or wood. In these cases, superficial cleaning is no longer sufficient and renovation can be very expensive. For this reason, it makes sense to take measures to prevent the development of mold at an early stage.
Mold prevention at a glance
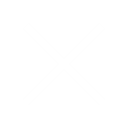
- Room temperature between 19 ° C and 21 ° C; the room temperature should not drop below 16 ° C
- Place larger pieces of furniture at a distance of 5 - 10 cm from the outer walls
- Intelligent ventilation concept, e.g. through a decentralized ventilation system
- Use breathable alkaline wall plasters and paints
- Keep doors in the apartment closed, especially in rooms that are heated to different degrees
- Keep windows closed during the heating process
- No indirect heating of colder through warmer rooms
- Ventilate for 5 - 10 minutes several times a day
- Do not dry laundry in the apartment
- Insulating thermal insulation of the house



Measures to prevent mold in living space
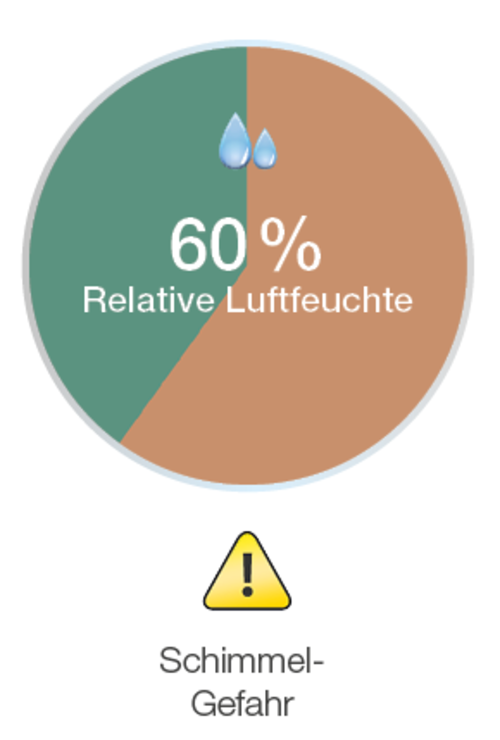
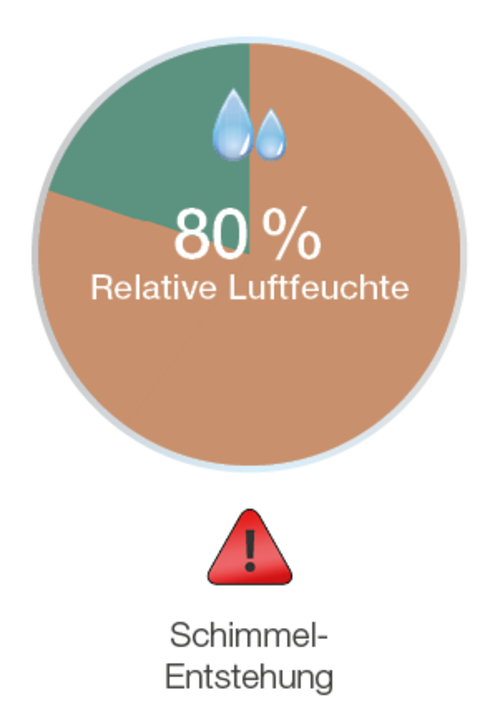
Mold growth occurs when the humidity in the apartment is too high. From a relative humidity of 60% there is an increased risk of mold, from 80% mold definitely occurs in the living rooms. It is therefore important to keep the humidity at an acceptable level in order to avoid mold growth on the surfaces.
The following measures can be used to regulate the humidity and, as a result, prevent mold growth. These relate on the one hand to one’s own behavior in the apartment, and on the other hand to structural and energetic measures.
Tips for preventing mold
Correct heating
With decreasing room temperature, the water absorption capacity of the air decreases and thus the relative humidity increases. For this reason, moisture collects on outer walls, in corners and on windows, as these areas are generally colder than the rest of the room. Especially in winter, when the difference between inside and outside temperature is large, these areas are particularly at risk of mold.
To reduce the risk of mold, the room temperature should be between 19 ° C and 21 ° C so that the walls do not cool down too much and water is deposited on them. Even in rooms that are rarely used, it is advisable to keep the temperature at at least 16 ° C, which is why the heating should never be switched off completely, even in winter.

Furthermore, tilting the window during the heating process should be avoided. With an open window, the neighboring surfaces cool down and condensation forms. Mold can easily develop in these areas.
Particularly in the case of differently heated rooms, it must also be ensured that the doors in the apartment remain closed. The warm air from the heated room otherwise flows into the colder rooms, in which the water absorption capacity of the air is lower due to the lower temperature. The relative humidity rises to a dangerous level and the excess water settles on the colder surfaces.
Especially after showering or cooking, it is better to keep the doors of the bathroom or kitchen closed, as the humidity rises to a significantly higher level than in the other rooms of the apartment due to the water vapors. In no case should cooler rooms be heated by warmer rooms, even if the belief persists that this will save heating costs.
Correct ventilation
In addition to heating, proper ventilation plays an important role in avoiding mold. A suitable room temperature ensures that the relative humidity does not exceed a critical level and that the outer walls do not cool down too much, so that no water settles. The absolute humidity cannot be regulated by the temperature. Over time, more and more water vapor collects in the air – for example through breathing – and this increases the likelihood that water will settle.
The absolute humidity in the room air must be reduced through correct ventilation. Especially in winter, when the temperature difference between the outside and inside area is very large, the warm, humid room air must be exchanged for fresh, colder air when ventilating in order to ensure reduced humidity. Basically, the room should be ventilated several times a day for 5 – 10 minutes.
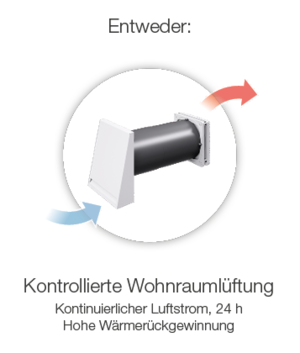
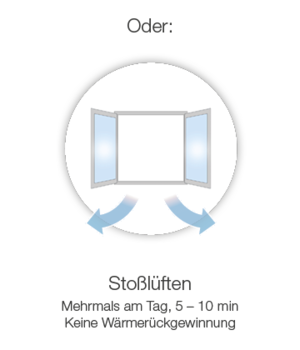
Further measures to prevent mold
Smaller measures also prevent the formation of mold. The aim is not to unnecessarily increase the humidity. For example, drying laundry in the home increases the humidity significantly and should therefore be avoided. If this is not possible, ensure that the room used is ventilated more often than usual in order to reduce the additional moisture. Another measure is not to keep the potting soil of indoor plants too wet or to replace moldy soil immediately. This also reduces the humidity. Storing firewood, which always contains some residual moisture, should also be avoided in the apartment – if possible.
Furthermore, the arrangement of the home furniture can promote mold growth. If there are larger pieces of furniture such as cupboards on the outside walls, which potentially cool down more easily, the air between the cupboard and the wall can no longer circulate and moisture is deposited and consequently mold forms. Furniture should therefore be placed at a distance of 5 – 10 cm from the outside walls.
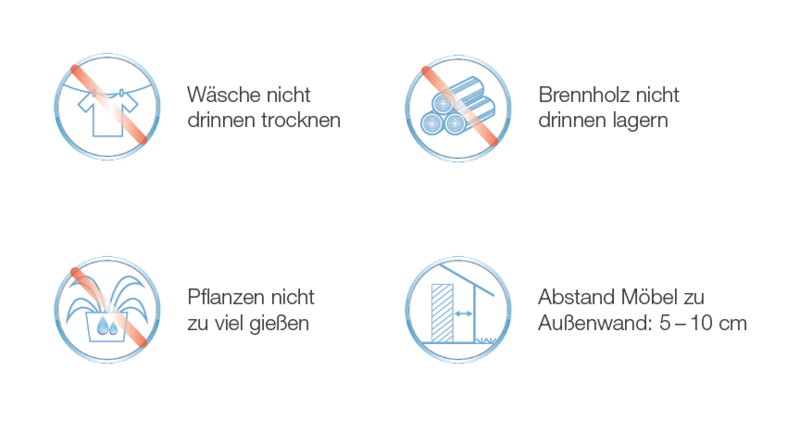
Structural and energetic measures to prevent mold
Thermal insulation, in particular interior insulation
New buildings and many energetically refurbished houses today mostly have thermal insulation. Thermal insulation ensures that the heat is retained in the apartment and that the indoor air does not circulate with the outdoor air. Contrary to the popular belief that this prevented air circulation leads to mold, thermal insulation actually prevents mold infestation in the apartment. Since the outer walls are kept warm, no moisture can settle and accordingly no areas for mold to attack. However, thermal insulation only makes sense with a suitable ventilation concept. Without a suitable ventilation system, the reduced circulation between indoor and outdoor air means that ventilation must be carried out more often, as the relative humidity increases more sharply than in unrenovated apartments.
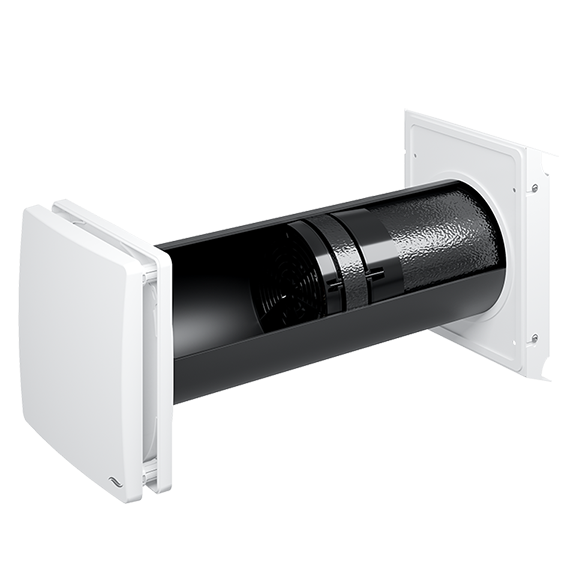


Intelligent ventilation system
Thermal insulation only has a preventive effect against mold if it is accompanied by a suitable ventilation concept. With an intelligent ventilation system, residents no longer have to worry about proper ventilation, as the indoor air is automatically exchanged and the humidity in the living spaces is reduced. It is important that the ventilation filters are replaced regularly.
Use diffusion-open, alkaline wall plasters and paints
Mold spores are always in the air and only spread when the humidity is too high and there are surfaces on which the mold can grow. On the one hand, preventive measures can be taken against mold by keeping the air humidity low; on the other hand, the surfaces can be prepared in such a way that no mold can build up there in the first place. An effective way of doing this is to use calcareous wall plasters and mineral paints for the walls. In contrast to plastic-containing wall plasters and emulsion paints, lime plaster and mineral paints are alkaline and thus form a surface on which mold cannot survive.

The mold expert Mike Hahn, expert for moisture and mold damage, advises: “Thermal insulation can prevent mold. By applying thermal insulation, there is a favorable shift in the isotherms in the outer wall. The consequences, provided that the rooms are adequately heated, are longer-lasting, higher wall surface temperatures, after which a possible damage-causing condensation loss is significantly minimized. In principle, the installation of ventilation systems makes sense. All buildings of the newer design as well as most of the old buildings are provided with tight, heat-insulating window elements. Window ventilation is often the only ventilation option. It is now up to the users themselves to ventilate properly and adequately. Ventilation systems make the ventilation of an apartment independent of use. In this way, moisture peaks (e.g. during the night or after using the bathroom in the morning) can be minimized and mold growth can be prevented. "

Conclusion - prevention and mold avoidance
With the measures mentioned, mold can be prevented in a simple manner. This not only saves laborious mold control, but also saves considerable costs for mold remediation. However, the measures to be taken must always be tailored to the circumstances of the living space so that mold prevention can be effective.